ERP and EDI: a practical guide to smooth integration
EDI IntegrationFrom ERP to EDI: Seamless data exchange for modern businesses
SAP, Microsoft Dynamics, Oracle, Sage, Epicor, Delegate, BMD — countless ERP systems compete for the attention of business customers worldwide. But to ensure these different systems can actually communicate with one another — in other words, exchange data with business partners such as customers or suppliers in a structured way — an EDI solution is almost always required.
Harald Hübler, Solutions Engineer at EDITEL, explains why many ERP systems can only unlock their full digitalization potential with an EDI integration, what benefits this brings, how the integration process works, and what companies should look for when choosing the right EDI partner.
Why should companies that use or plan to implement an ERP system consider EDI integration from the very beginning?
Efficient and seamless communication between companies is becoming increasingly critical in today’s digital business world. ERP systems are designed to combine multiple processing steps into a single workflow and centralize data. By integrating EDI, data exchange is automated — which offers major advantages, especially in logistics and supply chain management between two or more business partners.
What are the main benefits?
In a nutshell: EDI simplifies and accelerates communication within supply chains. An EDI-based process enables automated data exchange. This means that business documents such as purchase orders (ORDERS), dispatch advices (DESADV), or invoices (INVOIC) draw directly on existing data from the ERP system. As a result, data quality increases, manual transactions are eliminated, sources of error are minimized, and processing times are significantly reduced. Transmitting business documents and data through an EDI solution can substantially speed up business cycles. The key advantage lies in the automated interaction between EDI and ERP systems, which optimizes business processes overall.
Does this also create strategic advantages?
Absolutely. Since modern EDI systems can integrate with other enterprise tools and platforms — such as ERP systems — they provide better business insights and make analytics easier. Companies can make decisions faster and respond more quickly to changes in market or customer demands. In addition, EDI simplifies the onboarding of new business partners worldwide because it provides a shared business language that ensures consistent communication across systems and borders.
What prerequisites should an existing ERP system meet to enable EDI integration?
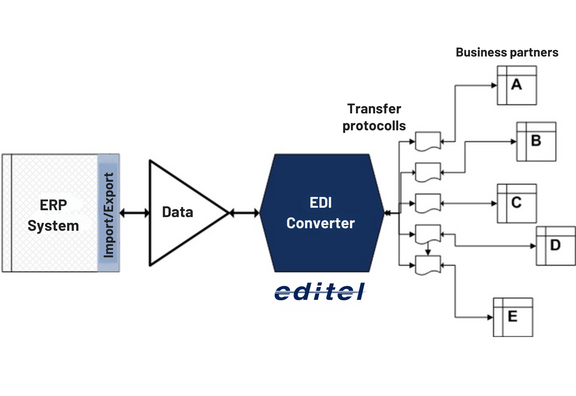
Ideally, EDI-related requirements are considered as early as the ERP implementation phase. However, this doesn’t mean that later integration is impossible — quite the opposite. The most important component of any EDI integration into an ERP system is the import and export of structured data. Within the ERP system, this is managed via an import/export interface. In most cases, ERP vendors offer this as an EDI module. Typically, ERP systems don’t generate EDIFACT files directly; instead, they use an in-house format that is then converted into the appropriate format for each partner with the help of an EDI converter (EDI provider).
The diagram below illustrates the process in simplified form:
How does EDI integration into an ERP system work?
To ensure that EDI integration runs smoothly and meets the requirements of all business partners, several key steps are needed — from evaluation to implementation. The first step is to identify the relevant business processes. This involves determining which documents and transactions should be handled via EDI — in other words, which integration scenarios are required to automate communication with business partners.
Next, the EDI workflows and documents are configured. This includes defining message formats, protocols, conversion rules, and validation steps to ensure that data is exchanged accurately and in a standardized way. If necessary, the existing ERP system is also adapted — for instance, by setting up interfaces or integrating databases. Before the new system goes live, it undergoes thorough testing to ensure everything runs flawlessly.
Which standardized message types are commonly used?
That depends on the specific customer requirements and the procurement processes to be mapped. The structure of exchanged messages is precisely defined in EDI standards. Below are some of the most commonly used EDIFACT message types:
Product master data: PRICAT
Purchase orders: ORDERS
Order confirmations: ORDERSP
Dispatch advices from suppliers to buyers: DESADV
Delivery instructions: INSDES
Inventory reports: INVRPT
Receiving advice messages: RECADV
Invoices: INVOIC
…and many more. Of course, there are numerous other message types, but listing them all would go beyond the scope of this blog post.
What are the most important factors for a successful integration?
There’s one crucial point: integration can only be successful if the company thoroughly understands its internal infrastructure and processes. This requires deep expertise in identifying and mapping business processes along with extensive hands-on experience. At EDITEL, we’ve implemented countless EDI integrations across a wide range of ERP systems over the past decades. One key to our success has always been close communication with our clients. Only by understanding their internal processes in detail can we design the perfect solution. As the saying goes: “Good communication is the key to collaboration.”
What should companies look for when choosing the right EDI partner?
There are several aspects that play an important role:
Experience and track record: How long has the EDI provider been active on the market, and what kind of projects have they completed? At EDITEL, we can draw on a long-standing, highly experienced team with decades of expertise.
International reach: For companies with cross-border relationships between customers and suppliers, the provider’s international expertise is essential. This is worth considering even if your company currently operates only in Austria but plans to expand into other markets in the future.
Service and support: Evaluate the range of consulting and support services offered beyond standard EDI implementation. How quickly are experts available when you need help?
Process expertise and collaboration: The provider should have in-depth knowledge of process management in various IT environments and be willing to work directly with your suppliers to ensure seamless cooperation.
Quality and data security: Last but not least, high standards and regular audits are critical to ensuring reliability and data protection.
EDITEL meets all these requirements. For more than 40 years, we have been building digital bridges, continuously helping our clients optimize their value chains. Our solutions are backed by extensive international expertise, and we serve clients in nearly every European country, combining local market knowledge with global reach. With our 24/7 customer support, we also offer a service level that truly stands out.
Need more information? Our team will be happy to provide expert advice and support.
To learn more about solutions by EDITEL, please visit our overview page.

Harald Huebler
EDI Solutions Manager